Building a Rule-Based File Renaming Engine for High-Volume Project Data Management
Client background
Our client is a technology company focused on creating advanced software solutions to help users repair, optimize, and maintain their computers for long-term performance and reliability. Founded with a user-first philosophy, the company’s mission is to make PC care simple, accessible, and effective for everyone — from everyday users to IT professionals.
Problem background
Managing extensive collections of project files — such as images, logs, and generated datasets — often demands the ability to rename hundreds or even thousands of items in a consistent, structured, and meaningful manner. Traditionally, this process relies on manual editing or ad-hoc external scripts, which frequently result in inconsistent naming practices, accidental overwrites, and significant time inefficiencies.
Business challenge
The goal was to create a safe, flexible, and high-performance bulk file renaming system integrated directly into the main application.
This system needed to handle complex naming rules while providing real-time feedback and guarantees against filename collisions or invalid outputs.
Specific challenges included
- Supporting multiple rule combinations to cover advanced renaming logic
- Preventing duplicate or invalid filenames across directories
- Allowing real-time previews so users could verify results before applying changes
- Ensuring scalability for thousands of files without blocking the user interface
How did we make it work?
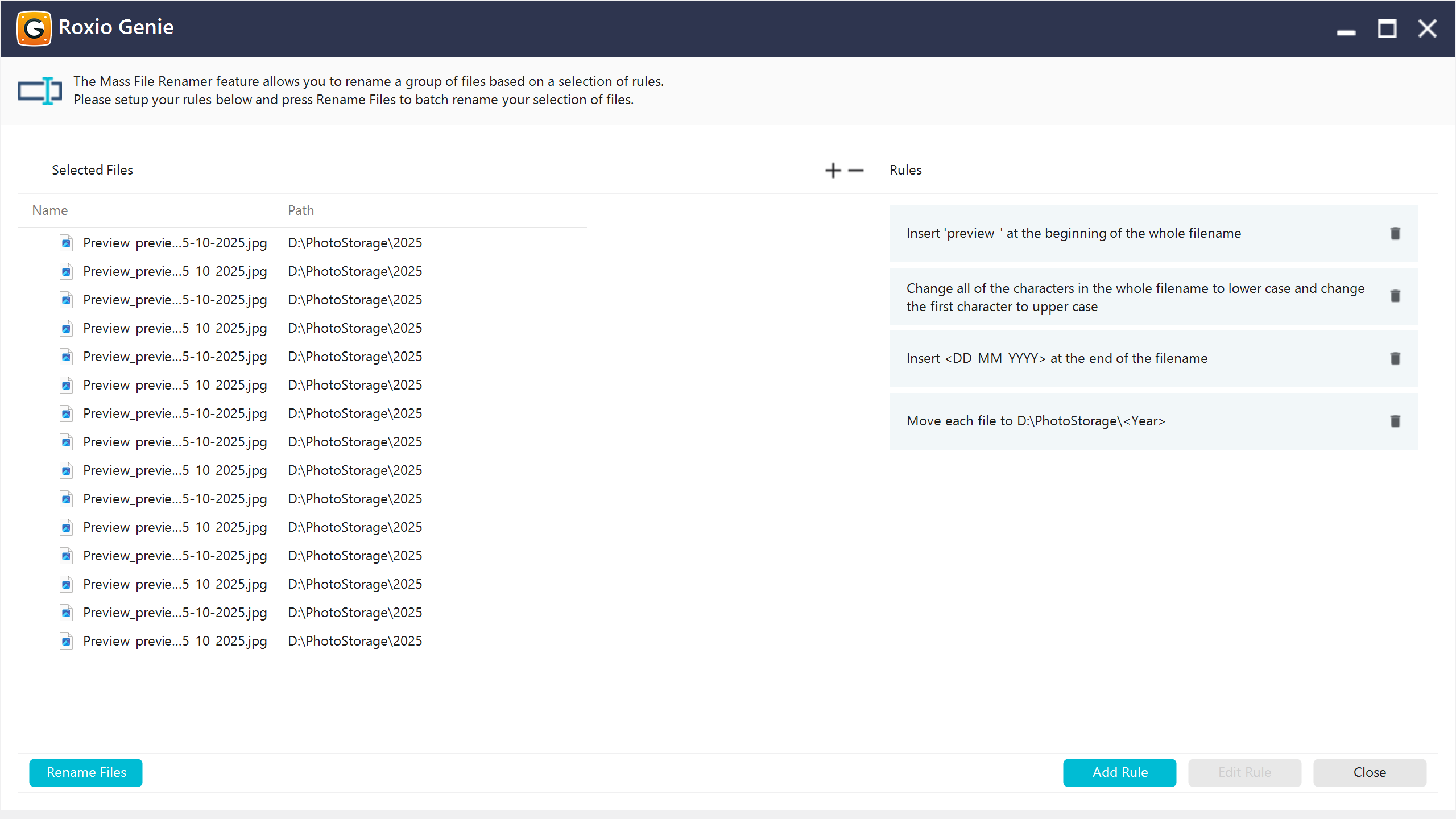
The feature introduced a rule-based renaming engine module integrated into the main application. The rule-based engine allowed combining rules, so complex renaming flows were possible. Rules were split into several categories:
Change case
Modified the letter case of filenames. Options typically included uppercase, lowercase, capitalize first letter, or title case. This was useful for maintaining consistent naming across systems that were case-sensitive.
Change extension
Replaced or removed the file extension for selected files. This helped when converting file types or standardizing extensions, processing sets of intermediate or temporary files, etc.
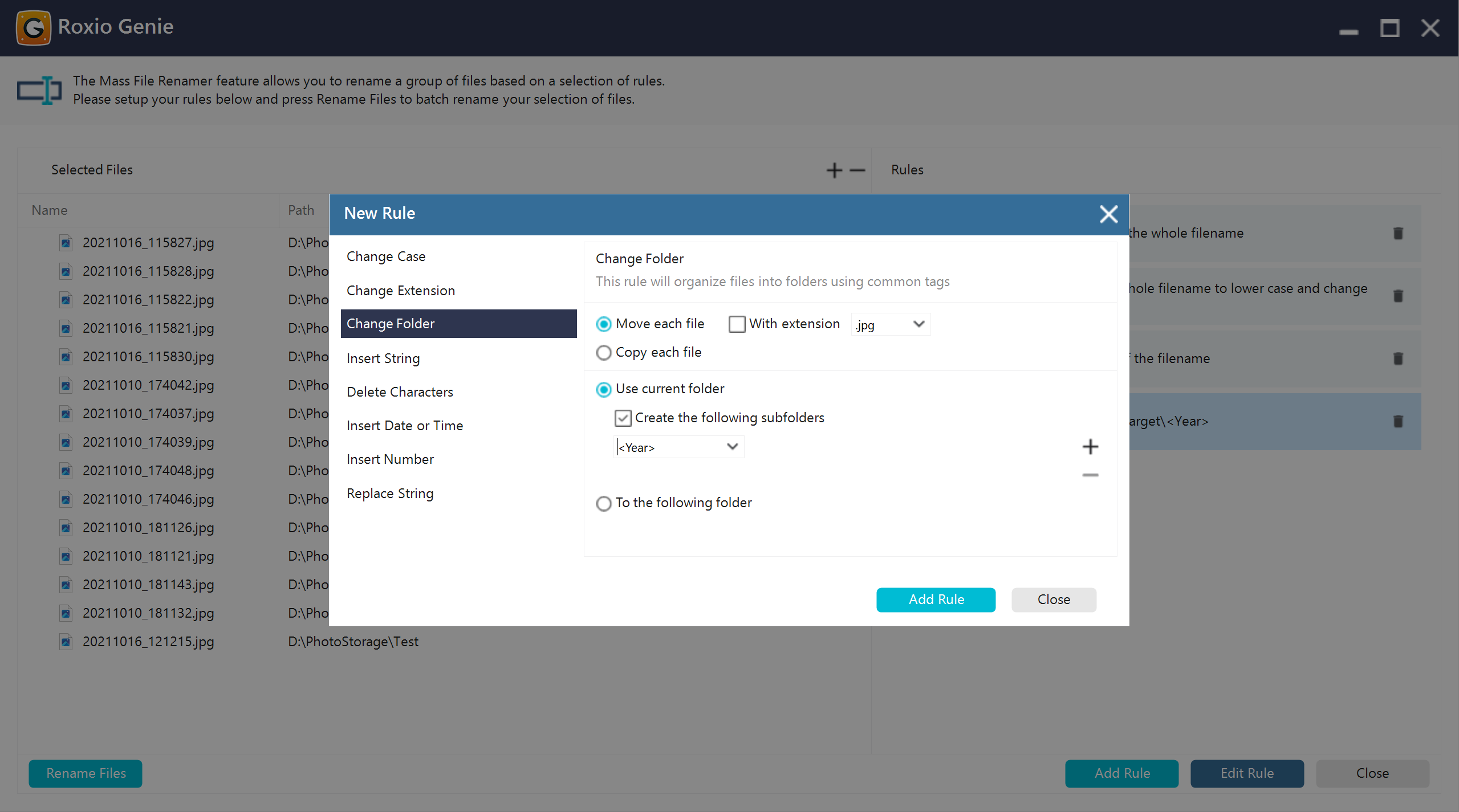
Change folder
Moved or reassigned files to a different target directory as part of the renaming process. This was useful for organizing files into new category folders or restructuring project hierarchies.
Insert string
Added a custom text segment at a specified position in the filename (for example, inserting a project code, prefix, or suffix). This was ideal for batch-tagging files.
Delete characters
Removed a defined range of characters from filenames. It supported simple position-based deletion to clean up unwanted parts.
Insert date or time
Automatically added the current or file-specific date/time to the name (e.g., creation date, modification date). This was commonly used for versioning or timestamped backups.
Insert number
Allowed appending, inserting, or prefixing incremental/decremental numbering to filenames. It supported custom start values, making it easy to create ordered sequences like photo_1.jpg, photo_2.jpg, etc.
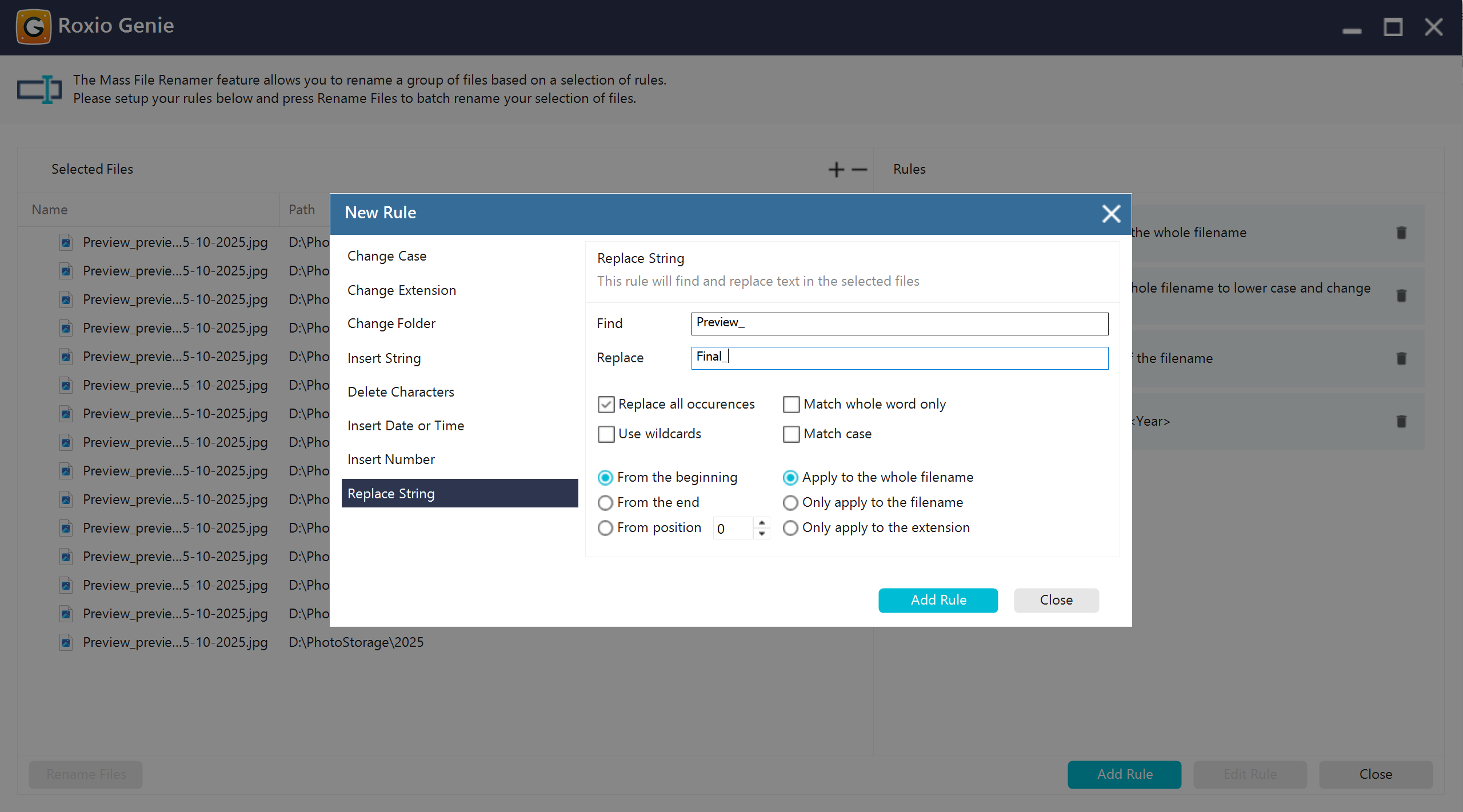
Replace string
Found and replaced a text fragment within filenames. It supported simple substring replacement or wildcards for more complex substitutions.
Technical approach
The renaming system was implemented using a transactional architecture, ensuring atomic operations — either all changes succeed or none do.
The engine runs asynchronously, preventing UI blocking, even when renaming thousands of files simultaneously.
It also provides pre-validation and live previews, enabling users to confirm results before committing changes.
To guarantee reliability, every operation can be rolled back if needed, preserving original filenames and avoiding data loss.
Key achievements
The rule-based engine transformed bulk file management from a time-consuming manual task into a fast, reliable, and predictable process.
Error reduction: Built-in validation and previews eliminate accidental naming conflicts
Time efficiency: Operations that previously took hours can now be completed in seconds
Consistency: Ensures standardized naming conventions across teams and projects
Scalability: Processes thousands of files without blocking the interface or filesystem
Reliability: Transactional safety and rollback capabilities guarantee secure operations
Value delivered by devPulse
- Flexible rule-based design enables complex multi-step renaming flows
- Real-time preview and validation ensure accuracy before execution
- Modular, composable architecture supports future extensions and new rule types
- Smart automation replaces manual renaming, saving time and reducing human error
- Transactional safety model guarantees reversible, non-destructive operations
Development Timeline
6 months
Team Composition
- 3 developers
- 2 QA
- 1 PM
- 1 designer
Technology
- С++
- Boost
- COM
- WTL
- WinAPI
Location
Canada
Vlad and the DevPulse team have been amazing to work with over the last couple of years. You'd be hard-pressed to find a more talented, trustworthy and hardworking group of professionals who are dedicated to delivering quality work, innovation and successful outcomes for the business. Their camaraderie and resilience is admirable. Highly recommend this team for any software and web development projects!

Validate Your Product Vision and Prepare for Confident Development